Scientists develop new technology platform to detect SARS-CoV-2 by fluorescence readout
Atham from scientists has developed a new technology platform for pathogenial fluorometric detection such as a virus with a measurement of neon light emitted. The potential of new technology has been shown for SARS-COV-2 detection.
This technology platform can also be used to detect other DNA / RNA pathogens such as HIV, influenza, HCV, Zika, Ebola, bacteria, and other / developing pathogens.
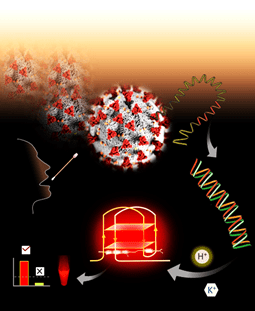
Viruses are the main global threat to human health, and the ongoing Covid-19 pandemic caused by SARS-COV-2 continues to cause disaster effects on all aspects of our lives. The unprecedented level of RNA virus transmission has required a quick and accurate diagnosis to facilitate contact searches (prevent the spread) and to provide timely care, said an official statement.
Scientists from Jawaharlal Nehru Center for further scientific research (JNCASR), an autonomous institution of the Department of Science and Technology, the Government of India, along with scientists from IISC (India Institute of Science), has shown G-based Nuklap Acid Noncanonical Topology Quadruplex (GQ) Targeting a reliable Conformation Polymorphism platform (GQ-RCP) to diagnose Covid-19 clinical samples.
This work has been published recently in the journal ‘ACS Sensors’ and the team also submitted a patent for novel technology.
This platform provides a greater emphasis on the decomposition and systematic characterization of a series of unique interactions in nucleic acid to achieve a stable and reliable non-non-non-non-non-non-Non-RNA target. RCP-based target validation is a general and modular approach for the development of nulisist numonic nuclastic diagnostic platform for various pathogens, including bacteria and DNA / RNA viruses.
“RT-Q-PRCR has become a gold standard for accurate detection of SARS-COV-2 (Covid-19). Among recent innovations in the nucleic diagnosis targeted by SARS-COV-2 acid, techniques such as RT RPA and RT-Lamge use the probe of DNA sensing general purpose .
The team has identified and characterizes the unique G-Quadruplex-based target that comes from the Genome M 30 KB Landscape (Kilobytes) of SARS-COV-2 for SARS-COV-2 specific detection. Unlike other reliable diagnostic tests where the existing fundamental concepts have been rejected, this work presents a fully new strategy to target unique and unconventional structures specifically for SARS-COV-2 sequence using small molecular fluorophors (microscopic molecules).



Average Rating